CASE20250817_004
Very High Risk Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Abnomalous Origin of the Right Coronary Artery: A Case Report
By Duc Chinh Nguyen, Cong Dinh Pham, Phi Long Tran, Huong Thi Quynh Tran
Presenter
Huong Thi Quynh Tran
Authors
Duc Chinh Nguyen1, Cong Dinh Pham1, Phi Long Tran1, Huong Thi Quynh Tran1
Affiliation
Stroke International Services General Hospital, Vietnam1
View Study Report
CASE20250817_004
ACS/AMI - ACS/AMI
Very High Risk Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Abnomalous Origin of the Right Coronary Artery: A Case Report
Duc Chinh Nguyen1, Cong Dinh Pham1, Phi Long Tran1, Huong Thi Quynh Tran1
Stroke International Services General Hospital, Vietnam1
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 67-year-old man with chest pain and shortness of breath was admitted. The patient had chest pain beneath the sternum radiating to the left shoulder and shortness of breath seven days before hospitalization. Each episode lasted 10-20 minutes. He was admitted to the emergency department for additional examination and care. Physical examination indicated 45-degree jugular veins (+) while other examinations were not significant.
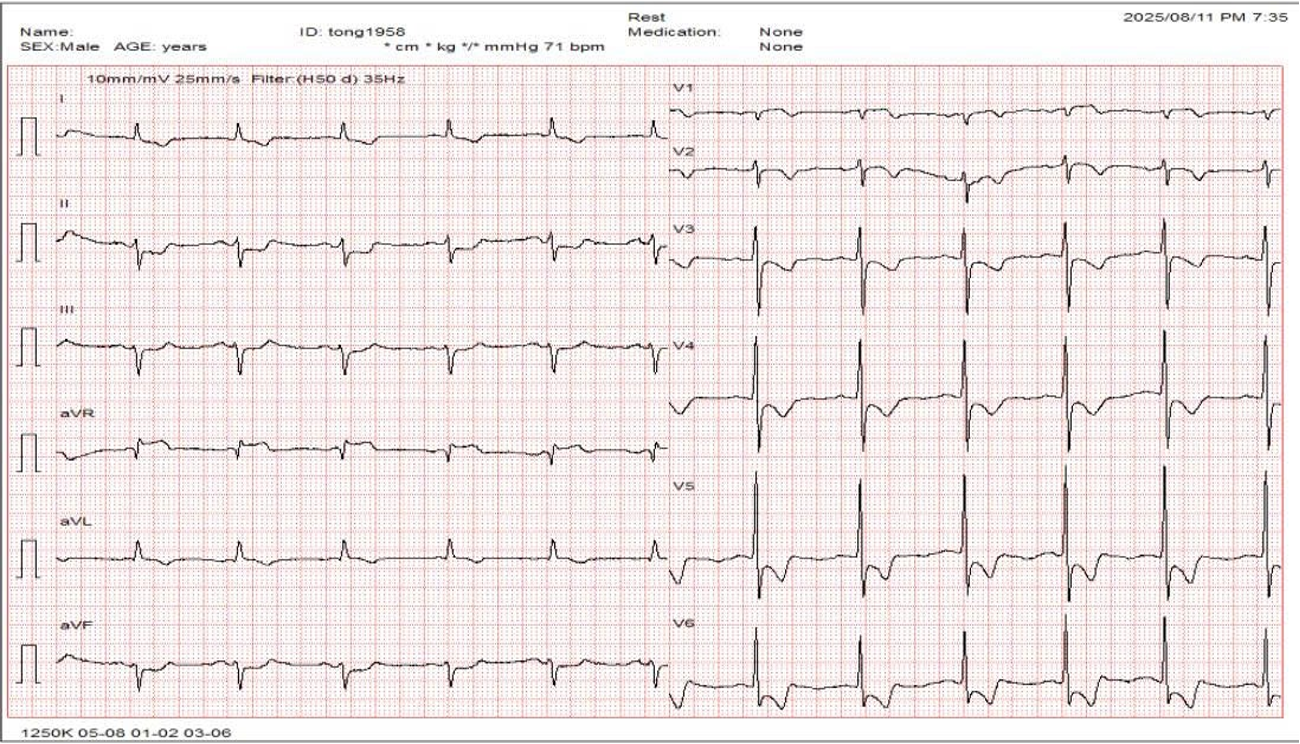

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
hs-TnI was 6.0 -> 86.6 pg/mL; NT-proBNP of 387.2 pg/mL. Echocardiogram showed hypokinesis of the lateral wall, left ventricular ejection fraction of 52%. No thrombus in the heart chambers, no pericardial effusion. Coronary CT angiography revealed an anomalous RCA origin arising 2 mm above the left coronary sinus from the aorta. CT-based reconstruction identified the optimal orthogonal viewing angle for the RCA ostium as RAO 22 °.
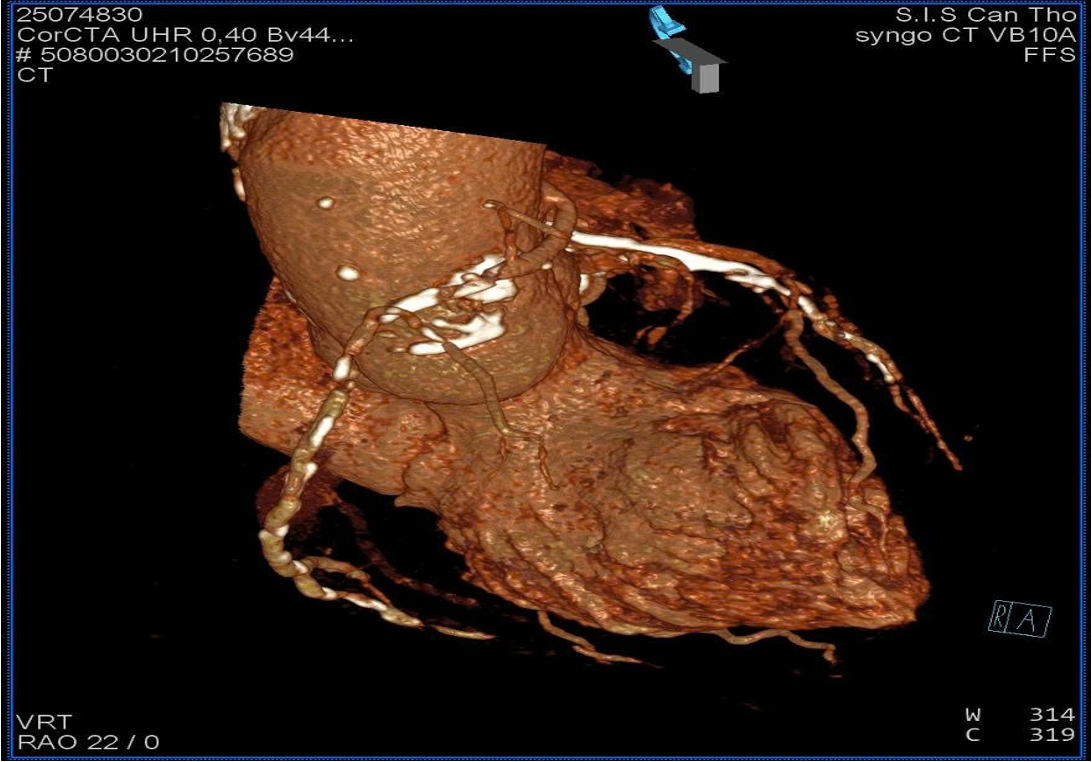
 PCCT 2.mp4
PCCT 2.mp4

Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiography of the RCA was initially attempted using a Tiger 3.5 5 F and a JR 4.0 5 F catheter but proved unsuccessful. A JL 3.5 5 F catheter was subsequently employed to selectively engage the left coronary sinus; however, after 30 minutes, selective cannulation could not be achieved. Guided by CTA findings, a JR 4.0 6 F guiding catheter was advanced, and with the gantry positioned at RAO 22 °, successful selective cannulation of the RCA was achieved with ease.
 DSA 1.mp4
DSA 1.mp4
 DSA 4.mp4
DSA 4.mp4
 DSA 6.mp4
DSA 6.mp4
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Percutaneous intervention of the right coronary artery was performed using a JR 4.0 6 F guiding catheter, with a Sion Blue wire advanced across the lesion with ease. However, due to severe calcification and an anomalous ostium with a sharp 90 ° angulation immediately after the take-off, additional support with a “mother-and-child” guiding catheter was required. Lesion preparation was carried out using a 2.0 × 15 mm compliant balloon, followed by sequential deployment of two drug-eluting stents: 2.5 × 26 mm and 3.0 × 24 mm. post-dilation was performed with non-compliant balloons sized 3.0 × 12 mm and 3.5 × 15 mm. Final angiography demonstrated optimal results with TIMI 3 flow.
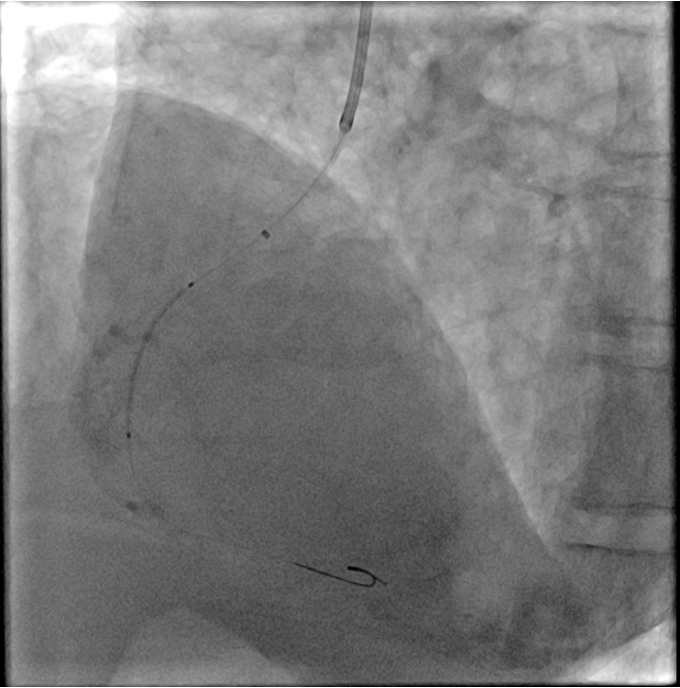
 PCI 6.mp4
PCI 6.mp4
 PCI 7.mp4
PCI 7.mp4

Case Summary
This case illustrates the difficulties of handling high-risk NSTEMI with an anomalous right coronary artery. Many coronary abnormalities are benign, but their occurrence in acute coronary syndromes might complicate diagnosis and treatment. The atypical RCA origin made catheter engagement difficult and protracted, which could have increased ischemia risk in our patient. These issues can be resolved with careful angiographic assessment, catheter selection, and imagin-based guidance. To enable timely and successful revascularization in high-risk situations, this case emphasizes anatomical variation prediction.
