CASE20250818_007
CTO Revisited: Redefining "Simplified" Antegrade Approach of Complex, Calcified CTO Lesions
By I Dewa Gde Dwi Sumajaya, Tsutomu Fujita
Presenter
I Dewa Gde Dwi Sumajaya
Authors
I Dewa Gde Dwi Sumajaya1, Tsutomu Fujita1
Affiliation
Bali International Hospital, Indonesia1
View Study Report
CASE20250818_007
Complex PCI - CTO
CTO Revisited: Redefining "Simplified" Antegrade Approach of Complex, Calcified CTO Lesions
I Dewa Gde Dwi Sumajaya1, Tsutomu Fujita1
Bali International Hospital, Indonesia1
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 68-year-old male patient was referred to our hospital for CTO intervention. The patient had experienced dyspnea on exertion for three months prior and occasionally felt chest heaviness. Physical examination was unremarkable, ECG showed Q wave at inferior lead, echocardiography showed normal ejection fraction. Coronary angiography revealed severe CAD 3VD with RCA CTO. Patient opted out for CABG, then LAD lesion was intervened. Patient still got symptoms, so tried to open RCA CTO in our centre.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
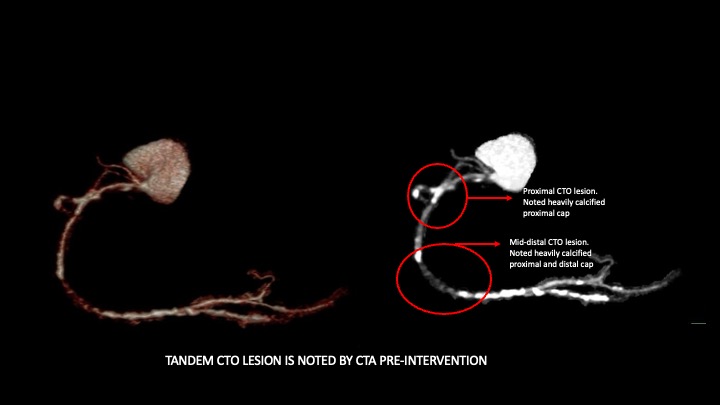
Prior to RCA CTO intervention, we performed CT coronary angiography to identify the proximal and distal cap. it turns out that RCA got tandem lesion with heavily calcified proximal cap with ambiguous entry and mid to distal RCA CTO lesion with distal calcified cap as well. This information would be particularly important to set the strategy for CTO crossing.

Relevant Catheterization Findings
From coronary angiography it shows RCA CTO with proximal ambiguous cap, distal filling from contralateral and shows distal tandem CTO before crux. The LCx is non dominant vessel with subtotal occlusion at ostial OM2. The LAD vessel diffusely disease with mild-moderate lesion at proximal, previously stented segment at mid to distal part still patent. There are some septal collaterals to distal RCA as well.
 LAD cranial view.mov
LAD cranial view.mov
 LCA RAO caudal view.mov
LCA RAO caudal view.mov
 RCA LAO view.mov
RCA LAO view.mov
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
We "simplified" this complex tandem calcified CTO lesion by using single injection antegrade 7Fr AL 0.75 guide catheter. We deliver wire into SB of ambiguous cap, then we attempted to puncture proximal cap with Pilot 200 guidewire preloaded into Corsair Pro microcatheter. Then we advance around 2-3mm of microcatheter then we did 1st HDR. Then we try to deliver Sion Black but failed. Then we change wire and diretion with UB 3 guidewire, then it looks cross the proximal cap, and we confirm by tip injection but eventually its going into another SB. Then we change entry position and attempting again with UB 3 guidewire but it couldnt cross because of tought CTO cap (as reflected from pre CTA evaluation). Then we change with ADR. We enter extraplaque by BASE technique and knuckling UB3 guidewire, but it difficult to cross then by Carlino technique, then we successfully deliver knuckle Sion Black guidewire into extraplaque space. Then we add another wire at subintimal by using DLC and deliver IVUS and found re-entry point which contain less calcium. Under live IVUS guidance we manipulate tip of wire (TD-ADR) and aim to puncture intraplaque by using CP12-ST preloading into Corsair Pro MC. Then after puncturing, we deliver microcatheter and confirm microcatheter position in intraplaque, then we advance Sion Black guidewire into distal vessel, and confirm true lumen by tip injection. Then we prepare the lesion, doing stenting (3DES) and evaluate the result by IVUS.
 mov-00093.mp4
mov-00093.mp4
 mov-00036.mp4
mov-00036.mp4
 mov-00054.mp4
mov-00054.mp4
Case Summary
Minimalistic CTO intervention in very complex calcified CTO is feasible. By utilizing HDR and TD-ADR will improve successfull rate of antegrade CTO intervention and by avoiding risk of retrograde approach. Tip injection is generally safe in controlled manner. By utilizing TD-ADR, we can precisely manipulate tip of wire under live IVUS guidance ant successfull rate is very high compare to controlled reentry by using Stingray balloon.
