CASE20250818_008
A Case of Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Guide Coronary Intervention of High-Risk Plaque and Stable Plaque in Coronary Artery Ectasia
By Chun-Yen Chiang
Presenter
Chun-Yen Chiang
Authors
Chun-Yen Chiang1
Affiliation
Chi-Mei Medical Center, Taiwan1
View Study Report
CASE20250818_008
Imaging & Physiology - Non-Invasive Imaging (CTA, MRI, Echo, etc)
A Case of Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Guide Coronary Intervention of High-Risk Plaque and Stable Plaque in Coronary Artery Ectasia
Chun-Yen Chiang1
Chi-Mei Medical Center, Taiwan1
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
The 54 years old male is a patient of hypertension and hyperlipidemia and coronary artery disease with regular medical therapy at our cardiovascular clinic. He received coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) on August 9, 2019, and there was significant stenoses with stable plaque at right coronary artery (RCA). He has no symptoms after medication. He received CCTA examinations on October 11, 2022 and July 1, 2025. The physical examinations of the patient showed unremarkable finding.


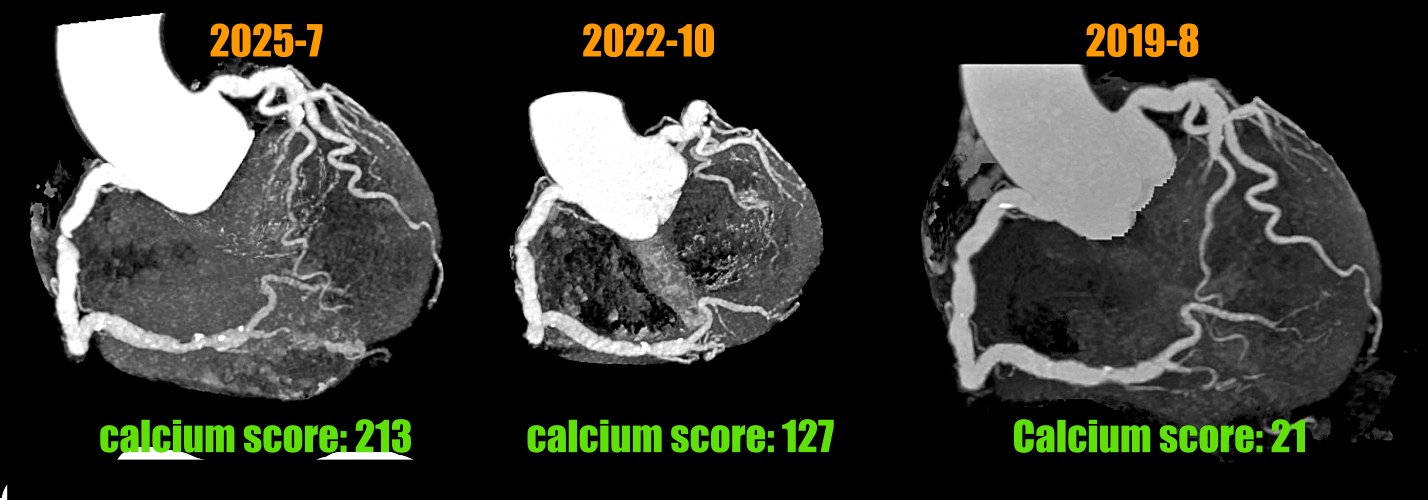
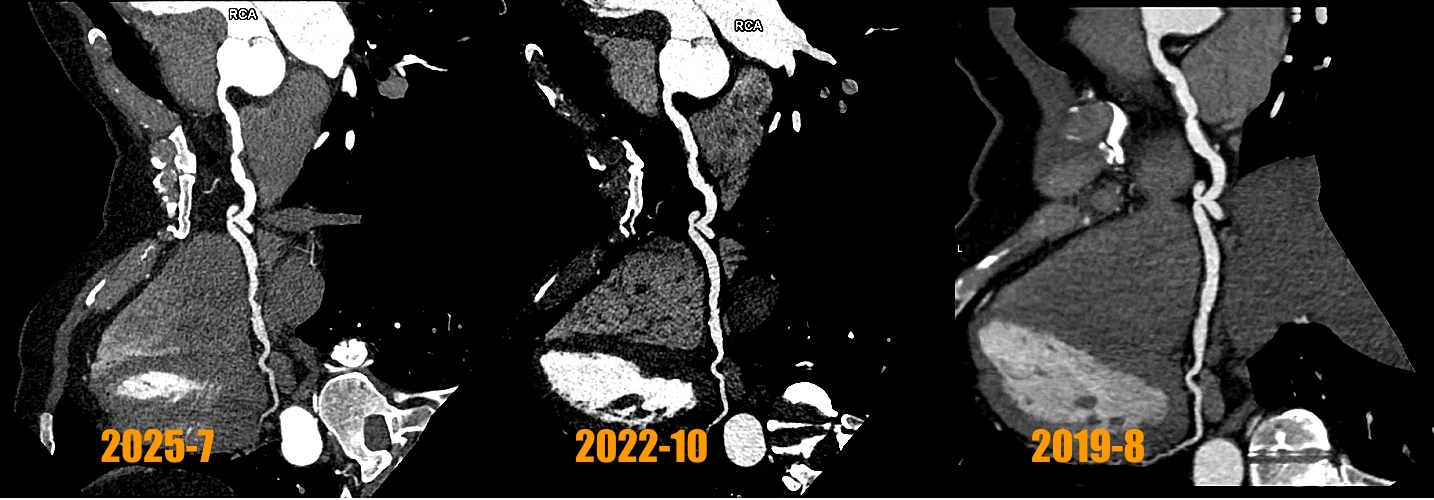
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
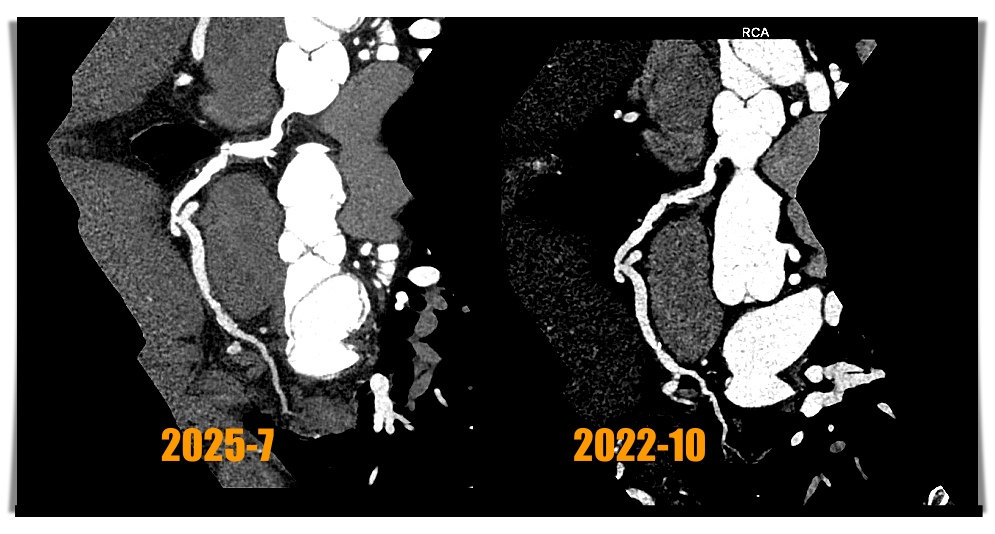
The third CCTA of the patient was performed on July 1, 2025 and showed calcium scores was 213 points (Fig 1) and coronary artery ectasia (CAE) of RCA and a 90% stenosis with high risk plaque with low-attenuation density and positive remodeling and spotty calcification at middle RCA (Fig 2 and 3) and a 80% stenosis with focal calcification and stable plaque at distal RCA. So regarding his RCA lesions of CCTA finding, the patient received coronary artery angiogram and coronary intervention.



Relevant Catheterization Findings
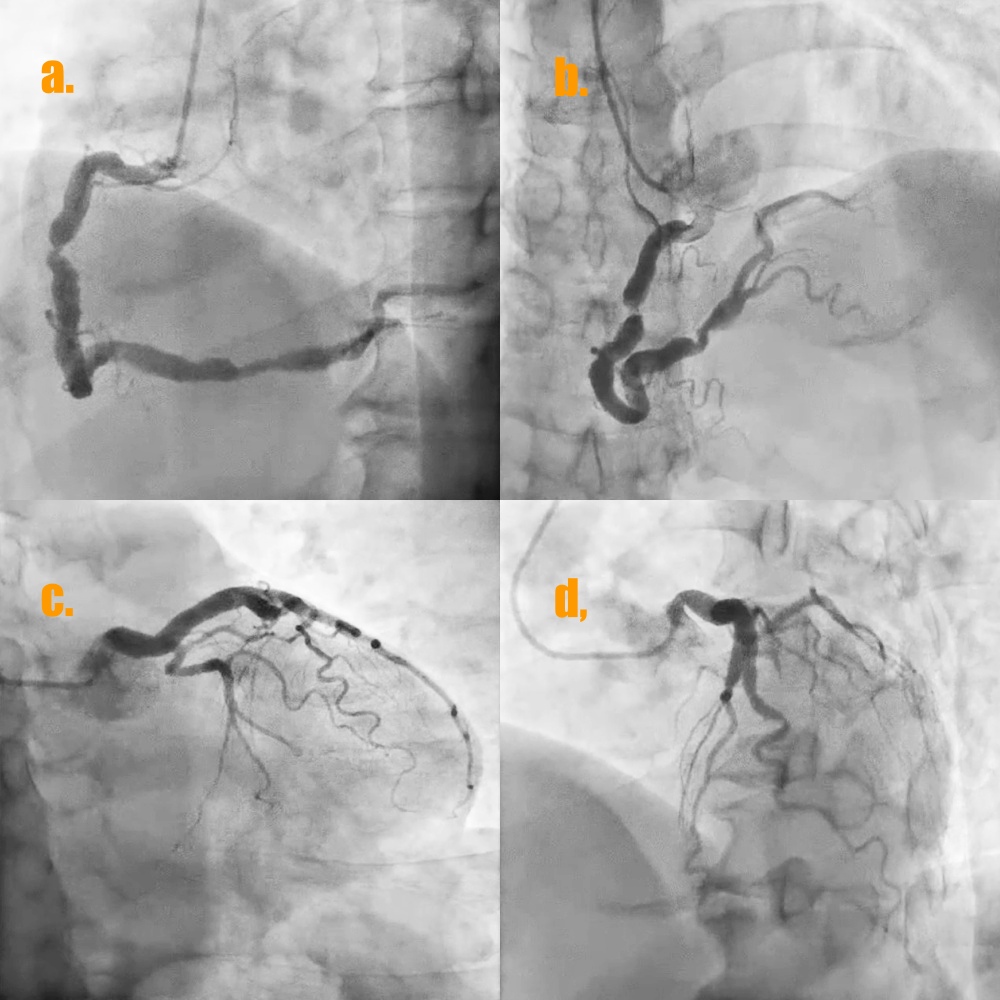
The coronary angiogram of the patient showed type 1 CAE of left anterior descending artery (LAD) and RCA (Fig 4a and 4d) and a significant stenosis with positive remodeling near coronary ectasia at middle RCA and another focal stenosis near coronary ectasia at distal RCA (video 1 and video 2) . In addition, there was much coronary thrombus with distal slow flow of coronary ectasia at distal RCA.
 Video 1. RCA in LAO view .mp4
Video 1. RCA in LAO view .mp4
 Video 2. RCA in cranial view.mp4
Video 2. RCA in cranial view.mp4

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
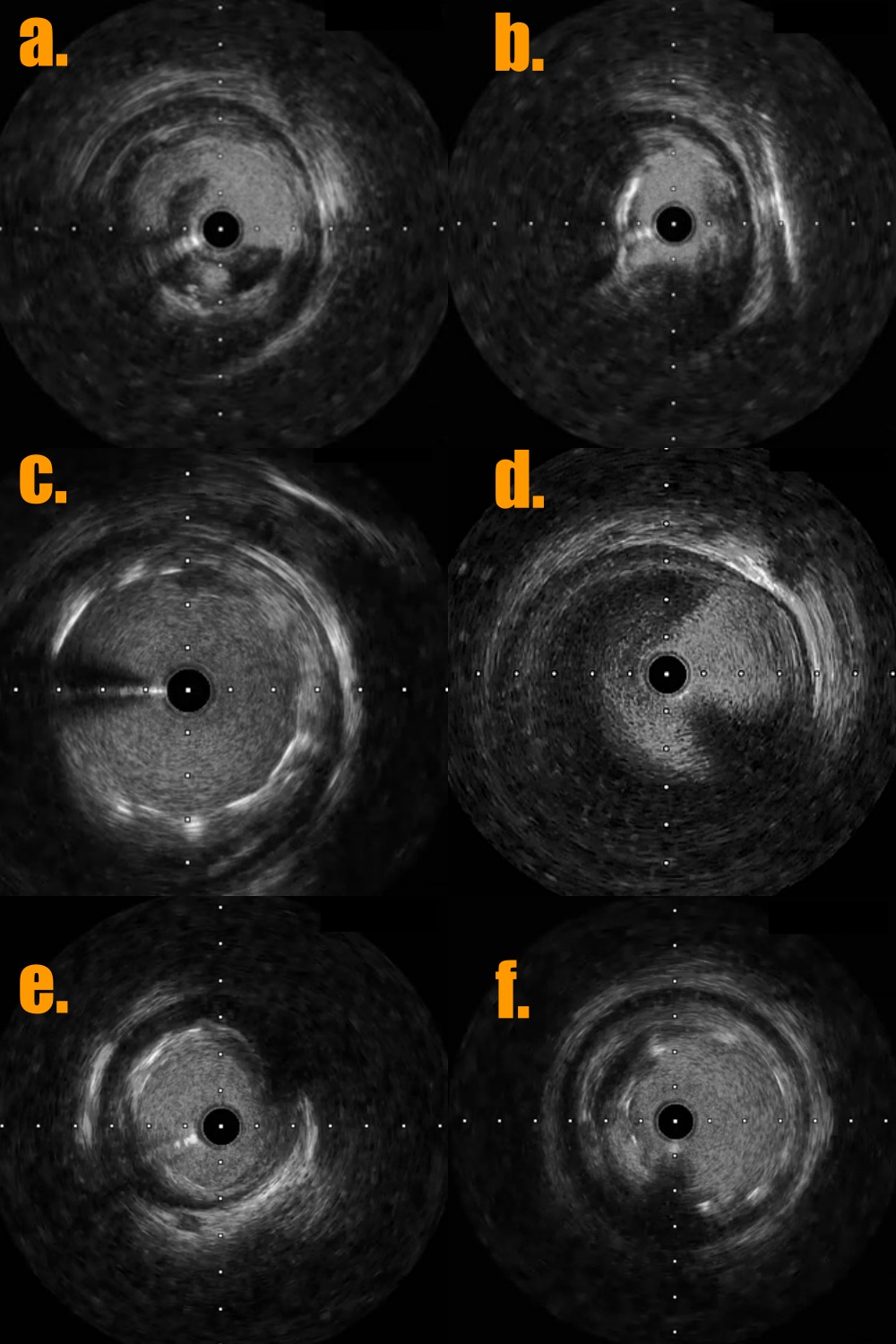
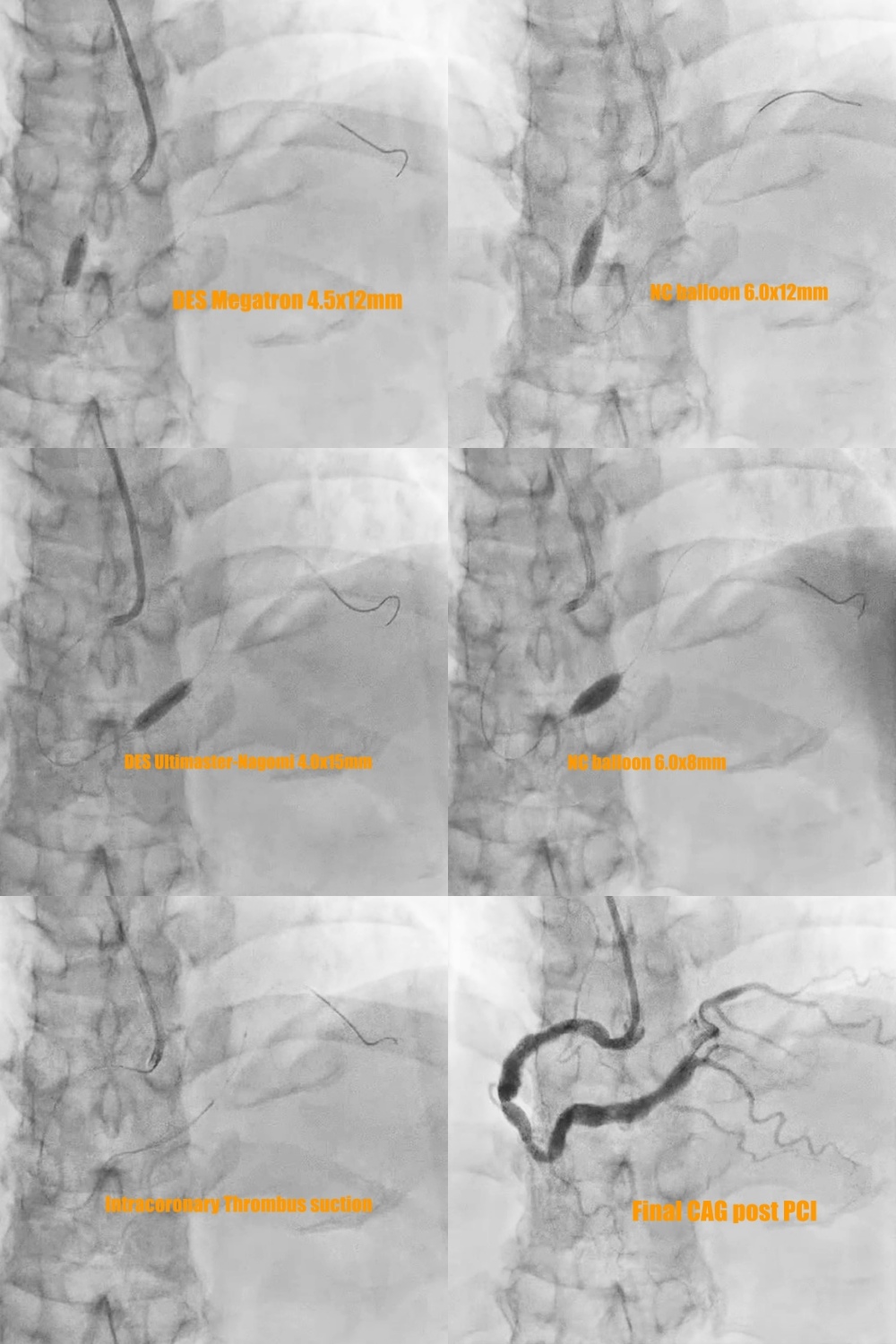
1. The 7 Fr left side radial sheath (Terumo; Glidesheath) was via left side radial artery approach and the guiding catheter was JR4 (Medtronic 7Fr) and the workhorse guidewire was Sion blue.2. Predilatation of the stenoses of distal part and middle part of RCA by the baloon Euphora 2.5x20mm and then IVUS was performed to assess the high risk plaque with adjacent CAE at middle RCA (Fig 5a and 5b) and stable plaque with adjacent CAE thrombus at distal RCA (Fig 5d and 5e).3. PCI of high risk plaque of middle RCA by direct DES stenting of Megatron (Boston ; 4.5x 12mm) under the extra-support of the guiding extension catheter of Telescope (Medtronic; 7 Fr) and lesion post-dilatation by larger balloon of NC Emerge (6.0x12mm) with 14 bars (Fig 6).
 Video 3.RCA post-PCI.mp4
Video 3.RCA post-PCI.mp4
4.. PCI of distal RCA lesion first by direct drug-eluting stent (DES) Ultimaster-Nagomi (Terumo; 4.0x15mm) and then post-dilatation by larger balloon NC Emerge (6.0x8mm) with 16 bars. There was coronary thrombus at coronary ectasia of distal RCA with slow distal flow (Fig 5d). The intra-coronary thrombus suction device of Export Advance (Terumo; 6 Fr) was into CAE site of distal RCA for maneuver thrombus suction several times but still residual thrombus at CAE (Fig 6).
5. The final coronary angiogram of RCA has good distal flow (video 3) with stent optimalization (Fig 5c and 5f)
6. Continuous heparinization 48 hours post PCI and triple therapy of DAPT and NOAC for 3 months and then de-escalation of NOAC and plavix for long-term drugs.


Case Summary
Regarding the atheromatous plaque with coronary artery ectasia in asymptomatic patients, coronary computed tomography angiogram is a good tool to evaluate the high risk plaque with the stenosis severity and guide the strategy of percutaneous coronary intervention or medical therapy.
