CASE20250820_007
Management of STEMI With Three-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease Complicated by Dissection: Stepwise PCI Including Left Main Side Branch DCB and Main Vessel Intervention
By Ji-Wung Ryu
Presenter
Ji-Wung Ryu
Authors
Ji-Wung Ryu1
Affiliation
Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart hospital, Korea (Republic of)1
View Study Report
CASE20250820_007
Complication Management - Complication Management
Management of STEMI With Three-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease Complicated by Dissection: Stepwise PCI Including Left Main Side Branch DCB and Main Vessel Intervention
Ji-Wung Ryu1
Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart hospital, Korea (Republic of)1
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 54-year-old female with a 10-year history of rheumatoid arthritis presented with acute chest pain persisting for 6 hours. She had no prior history of coronary artery disease, diabetes, or hypertension. On arrival, she appeared distressed with diaphoresis and hypotension. Blood pressure was 86/60 mmHg, heart rate 68 bpm, and oxygen saturation 92% on room air. ECG demonstrated ST-segment elevation in the inferior leads, consistent with acute inferior STEMI.
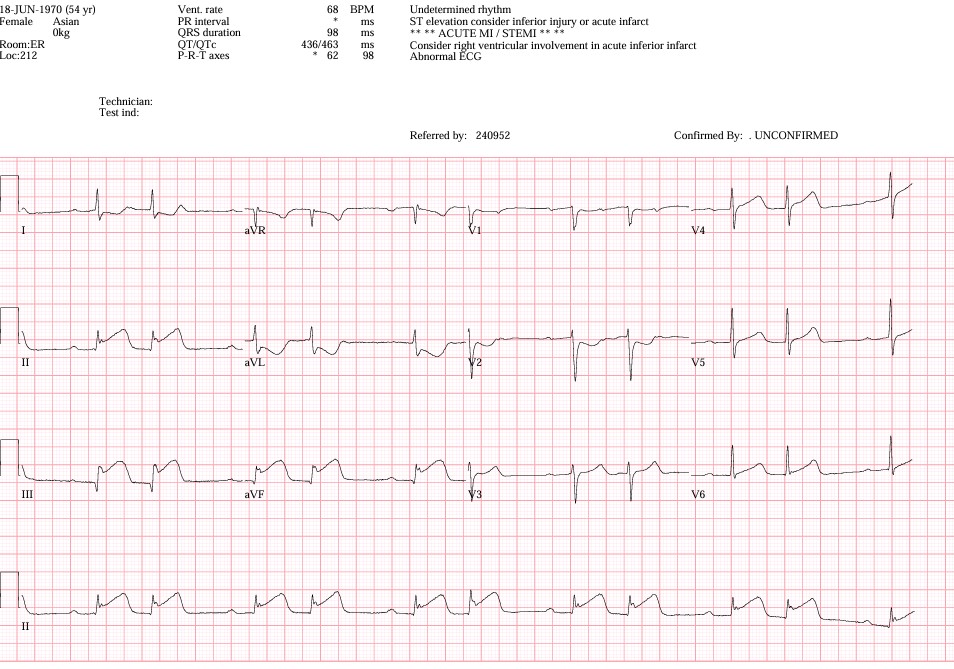

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Laboratory tests showed markedly elevated troponin-I (12.6 ng/mL) and CK-MB (48 U/L). Hemoglobin was 12.4 g/dL, platelets 218,000/µL, and creatinine 0.9 mg/dL. Lipid profile revealed LDL 118 mg/dL. Echocardiography demonstrated an ejection fraction of 42% with inferior wall hypokinesis.
 TTE1.wmv
TTE1.wmv
 TTE2.wmv
TTE2.wmv
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiography revealed triple-vessel disease with total occlusion of the proximal RCA as the culprit lesion, consistent with inferior STEMI. Significant stenoses were also noted at the left main bifurcation involving both the LAD and LCx. Initial PCI with stenting of the RCA was complicated by a major coronary dissection with hemodynamic compromise.
 CAG5.wmv
CAG5.wmv
 PCI10.wmv
PCI10.wmv
 PCI11.wmv
PCI11.wmv
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Primary PCI with stenting of the RCA was performed, but the procedure was complicated by a major coronary dissection, resulting in hemodynamic instability. After stabilization, a staged revascularization strategy was planned to address the complex residual disease. A rescue stent was implanted in the RCA to seal the dissection and restore distal flow. During the staged PCI, a drug-coated balloon (DCB) was applied to the proximal left circumflex artery (LCx) under intravascular imaging guidance, achieving adequate lesion preparation without flow-limiting dissection. Subsequently, a drug-eluting stent (DES, 3.5 × 18 mm) was implanted in the proximal left anterior descending artery (LAD) with high pressure, resulting in optimal stent expansion and apposition. Final angiography confirmed successful revascularization of both the LCx and LAD with preserved TIMI 3 flow.
 fu CAG1.wmv
fu CAG1.wmv
 2th PCI2.wmv
2th PCI2.wmv
 2th PCI7.wmv
2th PCI7.wmv
Case Summary
This case highlights the challenges of managing STEMI with multivessel disease complicated by major dissection during PCI. A stepwise approach using DCB for the left main side branch followed by DES implantation in the main vessel provided a safe and effective revascularization strategy, demonstrating the clinical feasibility of sequential intervention in complex PCI.
