CASE20250820_009
What to Do When Defragmenting a Retrograde Microcatheter During Recanalization of Ostial CTO?
By Emelianov Pavel, Sozykin Alexey , Shlykov Alexandr , Ul'yanova Lyudmila , Delikov Chingiz , Mkrtchyan Artur , Lozovskij Igor , Novikova Nataliya
Presenter
Emelianov Pavel
Authors
Emelianov Pavel1, Sozykin Alexey 1, Shlykov Alexandr 1, Ul'yanova Lyudmila 1, Delikov Chingiz 1, Mkrtchyan Artur 1, Lozovskij Igor 1, Novikova Nataliya 1
Affiliation
Petrovsky National Research Center of Surgery, Russian Federation1
View Study Report
CASE20250820_009
Complex PCI - CTO
What to Do When Defragmenting a Retrograde Microcatheter During Recanalization of Ostial CTO?
Emelianov Pavel1, Sozykin Alexey 1, Shlykov Alexandr 1, Ul'yanova Lyudmila 1, Delikov Chingiz 1, Mkrtchyan Artur 1, Lozovskij Igor 1, Novikova Nataliya 1
Petrovsky National Research Center of Surgery, Russian Federation1
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
a patient with a burdened cardiovascular history. Hypertension for a long time with a maximum increase of up to 200 and 100 mm Hg against the background of constant antihypertensive therapy, usual indicators within 115-120 and 70 mm Hg. In 2023, he suffered an ischemic stroke in the basin of the right SMA.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
The patient had a stress test –bicycle ergometry – outpatiently, the results of which were positive. The test was not completed. Itwas stopped at seventy five (75) Wolt because of complaints of pressing,squeezing pain in the heart region.

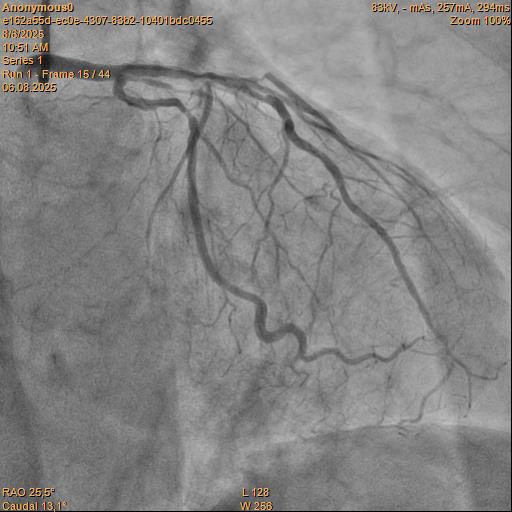
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Angiography Right coronary artery dominance LEFT CORONARY ARTERY (LCA): trunk of the left coronary artery: uneven contours along the entire length. Left Anterior descending artery (LAD): uneven contours, stenosis in medial part by 80%. Circumflex artery (LCX): uneven contours along the entire length. RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY (RCA): uneven contours in the proximal segment, Сhronic total occlusion, the post-occlusionportion is fairly filled through intersystem collaterals.
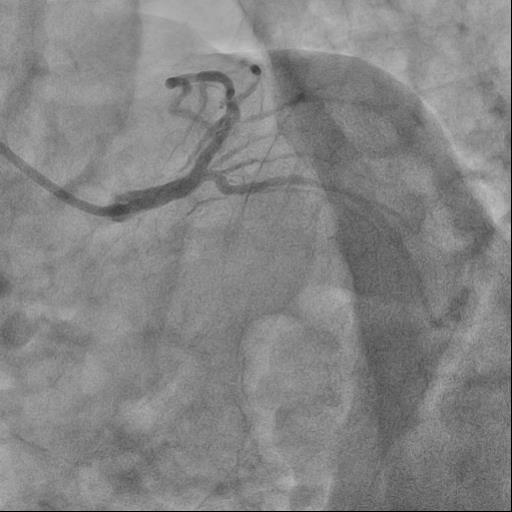
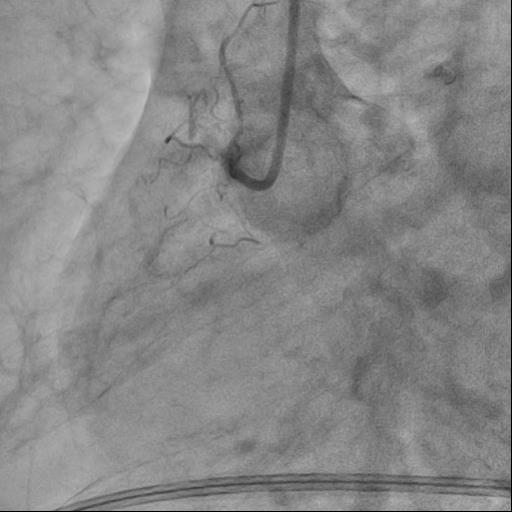



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
The guide catheter was selectively placed at the RCA orifice, several attempts at antegrade recanalization were performed, after 10 minutes a decision was made to perform retrograde recanalization of the RCA, Sion Blue with the support of a Corsair 150cm microcatheter was successfully introduced through the septal branch into the middle segment of the RCA, escalation to Gaya 2 was performed and recanalization of the RCA was performed. Tip-In was performed in the antegrade guide catheter, the retrograde coronary guide was fixed with a balloon catheter. The retrograde microcatheter was advanced into the proximal segment, however, when performing Corsair, its defragmentation occurred, and the tip of the microcatheter itself was torn off. A decision was made to perform repeated recanalization of the RCA in a new lumen. Recanalization was successfully performed, then Tip-In was performed into the antegrade microcatheter and its successful passage beyond the occluded area. Balloon angioplasty and stenting of the RCA under OCT control with vFR.
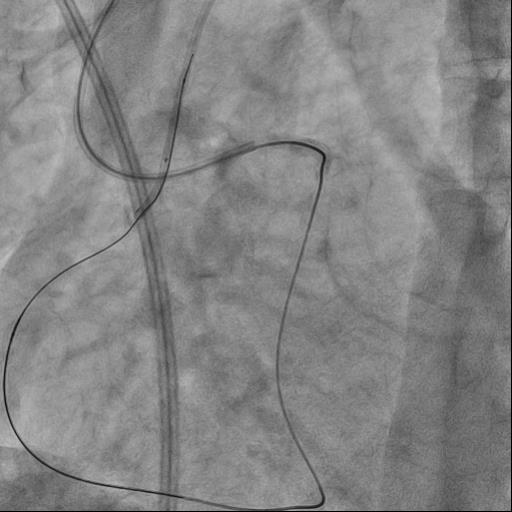
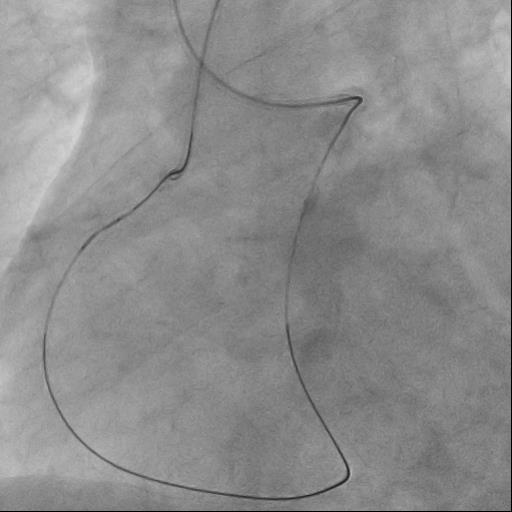
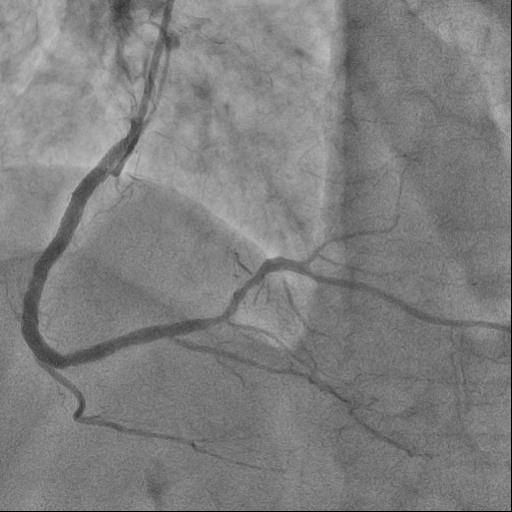



Case Summary
A) Antegrade progress during recanalization of the orifices of chronic occlusion of the coronary artery is important, however, changing the tactics to retrograde recanalization, when it’s absent, may further facilitate antegrade advance of the coronary guidewire, since the retrograde guidewire serves as a control point. B) If the retrograde intracoronary guidewire is well-controlled in the antegrade guide catheter, it is safer to use the tip-in technique in the antegrade microcatheter. It is preferable to perform the tip-in at the bend in the guide catheter, since both devices (the micro catheter and the coronary guidewire) are in the same plane.
