CASE20250903_005
Technical Challenges of Left Main PCI in the Presence of a Transcatheter Heart Valve
By Kyeong Won Seo
Presenter
Kyeong Won Seo
Authors
Kyeong Won Seo1
Affiliation
Asan Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)1
View Study Report
CASE20250903_005
Complex PCI - Left Main
Technical Challenges of Left Main PCI in the Presence of a Transcatheter Heart Valve
Kyeong Won Seo1
Asan Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)1
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
An 87-year-old female with a history of hypertension and dyslipidemia, previous PCI to the left anterior descending artery, and prior TAVR with a self-expanding Evolut 26 mm valve performed 7 years earlier presented with progressive exertional dyspnea.
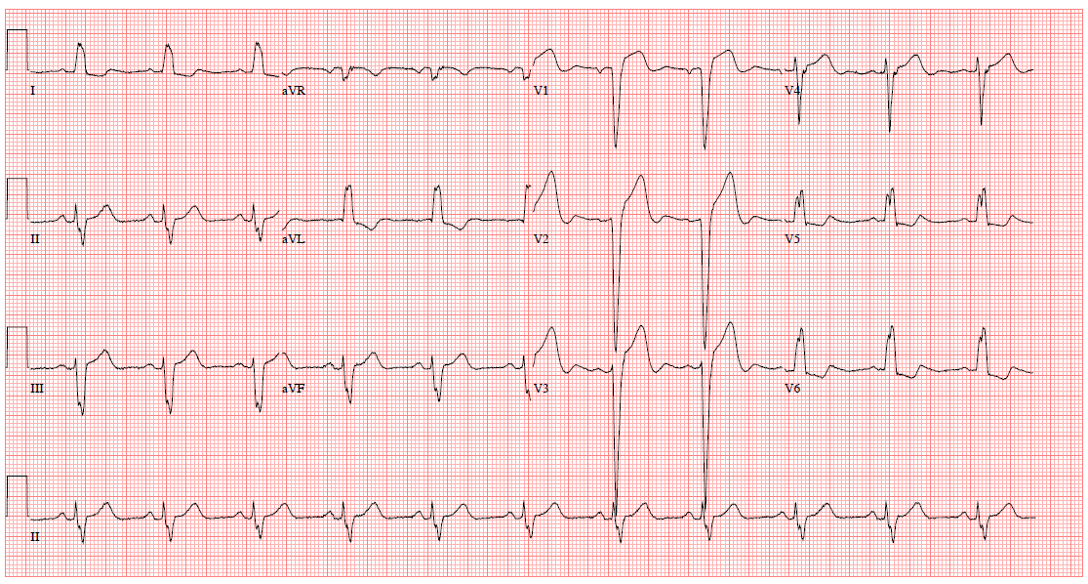
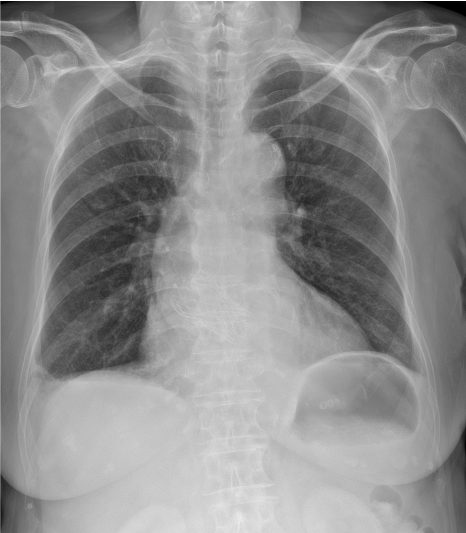


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Electrocardiography revealed left bundle branch block, and chest X-ray showed small amount of bilateral pleural effusion. Echocardiography revealed moderate to severe eccentric aortic regurgitation, moderate functional mitral regurgitation, and borderline left ventricular systolic dysfunction (EF 44%).
 3.mp4
3.mp4
 4.mp4
4.mp4
 5.mp4
5.mp4
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Coronary access was technically challenging due to the previous transcatheter valve frame, requiring guiding catheter downsizing from 7 Fr to 6 Fr to achieve stable engagement of the LM ostium. The LM–proximal LCX lesion was treated with drug-coated balloon angioplasty using Agent 3.0 × 15 mm. Subsequently, the LM–proximal LAD segment was treated with implantation of a 4.0 × 15 mm XIENCE Skypoint drug-eluting stent, achieving satisfactory expansion and apposition as confirmed by intravascular imaging. After successful coronary revascularization, staged valve-in-valve TAVR was performed using a 23 mm SAPIEN 3 Ultra valve.
 9.mp4
9.mp4
 10.mp4
10.mp4
 11.mp4
11.mp4
Case Summary
In patients with prior TAVR and LM bifurcation disease, careful catheter strategy, optimized PCI technique, and staged revascularization prior to ViV TAVR can enhance procedural success and clinical outcomes. Planning for future coronary access remains a critical component in ViV TAVR cases.
