CASE20210816_002
Shock Wave Lithotripsy in IVUS Guided PCI of Calcified Vessels
By
Presenter
Rohit Mody
Authors
1
Affiliation
, India1
Complex PCI - Calcified Lesion
Shock Wave Lithotripsy in IVUS Guided PCI of Calcified Vessels
1
, India1
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
case1- 141673 Case2- 167671
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Case1- 75 year old Male known case of Hypertension Diabetic AOE, DOE, Dyslipidemic, Restlessness Vitals StableCase2- 65 Year old Male Diabetic Known Case of Hypertension Hyperlipidemia AOE3 Vitals: Stable
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Case 1- Normal LV functionsCase 2- Normal LV Functions
Relevant Catheterization Findings
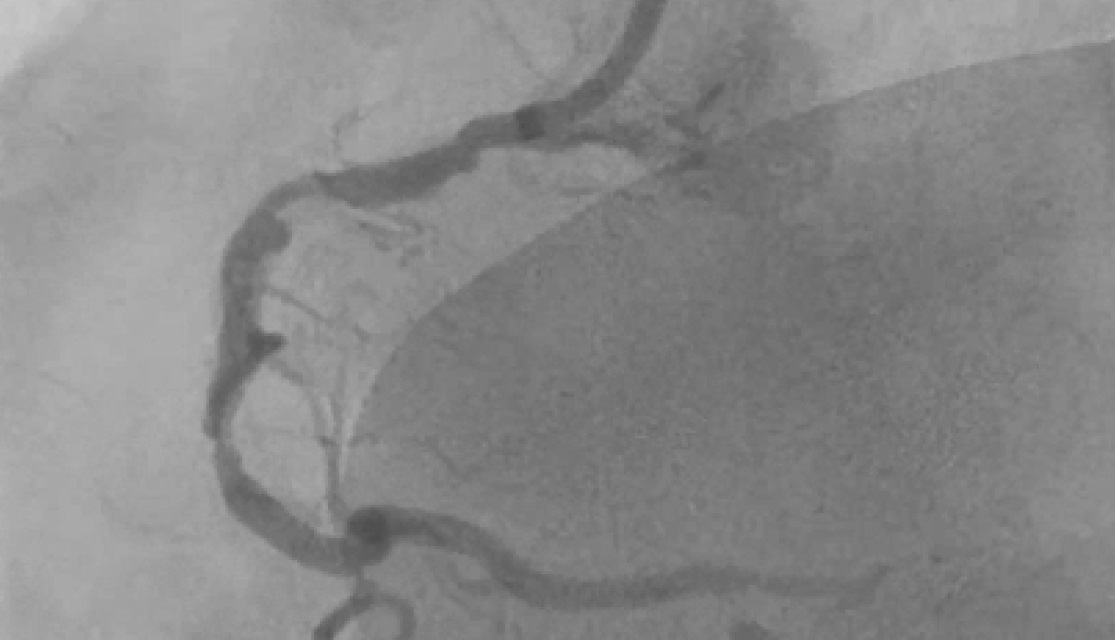
Case1- TVD, severe calcium in the vessels
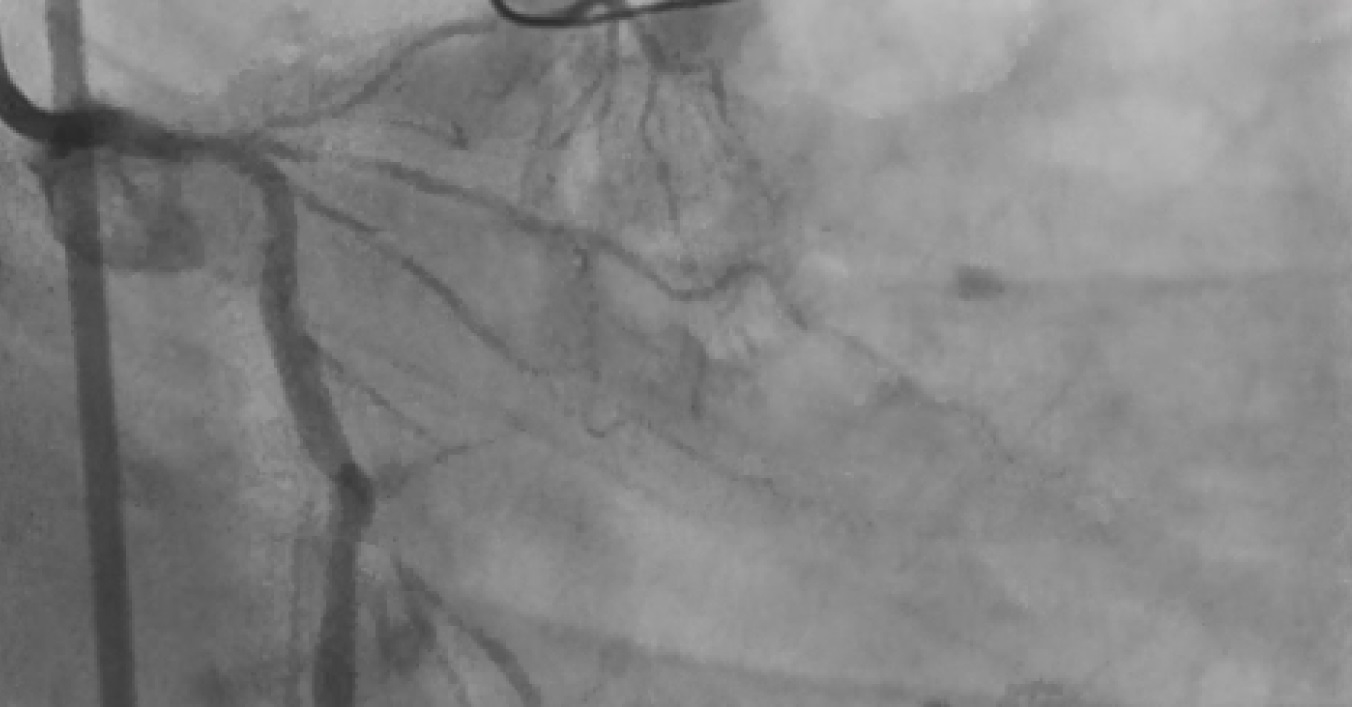
Case2- DVD, LAD 90% blocked. LCX 85% with severe calcification
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
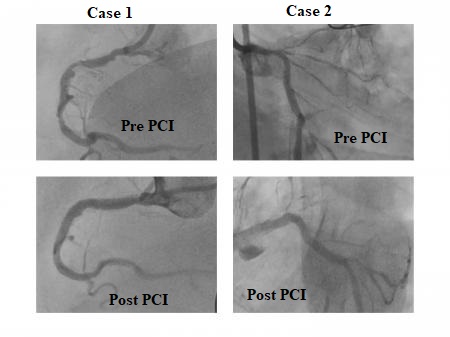
Case1- Stent Deployed in mid LAD, Crossed RCA Lesion with BMW wire, Pre Dilatation with 2.75X 10mm at 18atm, IVUS done, Shockwave Lithotripsy done with 3.0X15 mm balloon at 8ATM- 40 Pulses given on each site Distal to proximal, 3.5X28 mm Stent deployed in mid-RCA at 16ATM, Another DES 4.0X32mm deployed in ostial to Mid RCA, Post Dilatation 4.0X28mm Balloon at 18ATM Case2- Lesion in LCX crossed with BMW wire & pre dilated the lesion with 2.5X13mm Balloon at 18 atm, Lithotripsy in LMCA to LCX with 3.0X 15mm Balloon with 30 Pulses at each site, 3.5X32mm DES deployed in LMCA to LCX at 16atm, Post Dilatation 4.5X10mm Balloon,

Case Summary
Here we present our initial experience with the shock wave IVL system. We assume it an innovative technology where the calcified lesions, which were not amenable with other methods, were treated, and there appear to be lesser complications like perforations and no-reflow. In literature, S-IVL is found to be useful when the calcium is circumferential and superficial as well as deep. It’s efficacy in large vessel diameter and eccentric calcium is questionable. In our case, we found it to be useful for large diameters, deep calcium, and eccentric lesions as characterized by IVUS imaging.
