CASE20210824_003
Successful Percutaneous Coronary Intervention & Management of Coronary Dissection, Stent Entrapment, Dislodgement & Deformation in a Heavily Calcified Artery
By , , ,
Presenter
Bryan Rene Toledano
Authors
1, 1, 1, 1
Affiliation
, Philippines1
Complications - Complications
Successful Percutaneous Coronary Intervention & Management of Coronary Dissection, Stent Entrapment, Dislodgement & Deformation in a Heavily Calcified Artery
1, 1, 1, 1
, Philippines1
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
ES
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 81-year-old male was admitted due to chest pain and heart failure symptoms. He is a known hypertensive, dyslipidemic with a 15 pack smoking history. On physical examination he is tachypneic, apex beat at 5th left intercostal space anterior axillary line, no murmurs, positive abdominojugular reflux and bibasal rales were noted.
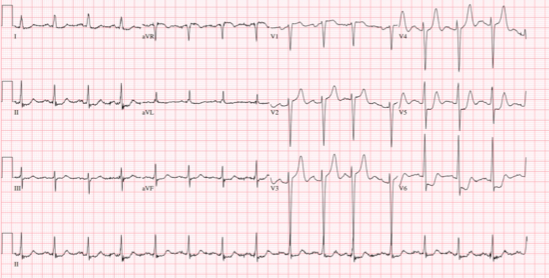

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
His 12L ECG showed sinus rhythm with peak T wave on leads v2-v5 and ST-segment depressions on leads v5-v6. Serial HS Troponin I showed increasing results 546-608-642pg/ml. His serum creatinine was stable at 0.79mg/dl and NT-pro BNP was elevated at 3257. Two-dimensional echocardiography showed no wall motion abnormalities and an ejection fraction of 54%.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
On fluoroscopy, the coronaries were heavily calcified. The LM is a 5mm vessel with 30% mid to distal segment stenoses. The LAD is a 4mm vessel with 99% ostial, 50% mid, and 30% distal segment stenoses. The LCX is a 3mm with 99% ostial segment stenosis. Both LAD and LCX provide Rentrop III collaterals to the RCA, posterolateral and posterior descending branches. The RCA is a 3.5mm vessel with 100% mid segment stenosis. An IABP and TPI were inserted prior to PCI.
 LAO CRA.mov
LAO CRA.mov
 LAO CAU.mov
LAO CAU.mov
 LAO RCA.mov
LAO RCA.mov
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
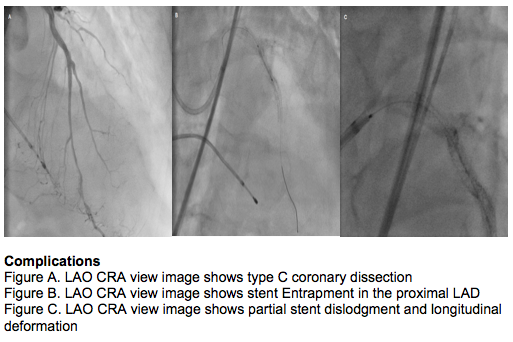
A 7F EBU 3.5 was used, Asahi Sion Blue wires distalized to the LAD and LCX. Predilation with balloon 2.0 x 20mm in the LAD-LM target lesions at 12-20 ATM. Using 3F OptiCross concentric calcific arch >270 in the proximal LAD was visualized. Several passes of rotational atherectomy with 1.75mm burr at 180,000 rpm in the proximal LAD was done. Another predilation using Non Compliant (NC) balloon 2.5 x 20mm in the target lesions at 12-20 ATM. A Drug Eluting Stent (DES) 3.0 x 24mm was deployed in the mid LAD at 12 ATM, overlapped with DES 3.0 x 20mm to the proximal LAD at 12 ATM and DES 3.5 x 24mm to the proximal LM at 12 ATM. Post dilation and proximal optimization using NC balloon 3.5 x 15mm in the proximal LAD-LM at 12-20 ATM was done. On post PCI angiography a type C coronary dissection was noted. Stenting of the dissection was planned however the DES 2.0 x 18mm was unable to pass the dissection and was entrap in the proximal LAD upon withdrawal. It was then deployed at 26 ATM, partial dislodgment, longitudinal stent deformation were noted on the previous LM DES hence a DES 3.5 x 16mm was deployed overlapped to the proximal LAD DES at 20 ATM followed by post dilation of the proximal LAD DES using NC balloon 3.5 x 15mm at 20 ATM. A compliant balloon 2.0 x 20mm was inflated in the dissection area for 20 secs. Post PCI IVUS and angiography showed complete stent apposition, LM MSA of 13.38mm2, ostial LAD MSA of 8.86mm2 and resolution of the above complications
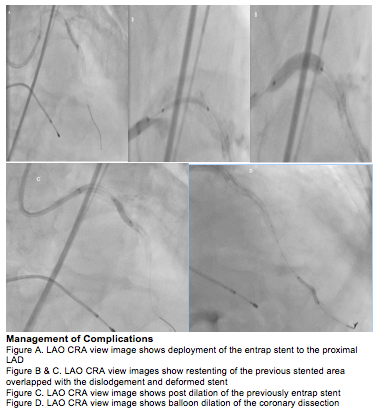
 Post PCI angiography.mov
Post PCI angiography.mov


Case Summary
In a heavily calcified coronary artery, percutaneous coronary intervention may lead to wire-induced dissection. A failed bailout stenting during withdrawal may cause left main stent partial dislodgment and longitudinal deformation from the untoward advancement of the guide catheter. In this scenario the entrap stent may then be deployed in an acceptable stent vessel size followed by post dilation and stent coverage of the previous stented area. A distal type C coronary dissection may be treated with balloon dilation and prolonged inflation. Intravascular ultrasound and angiography should be used to document the resolution of complications and proper stent apposition.
